
Articles - Year 1999 - Volume 14 -
Evaluation of the Nipple-areola Complex Sensibility after Reduction Mammaplasty by Superior Vertical Dermal Pedicle
Avaliação da Sensibilidade do Complexo Aréolo-Mamilar após Mamaplastia Redutora com Pedículo Dérmico Vertical Superior
ABSTRACT
Light touch by cotton wool and needle test were employed to evaluate nipple-areola complex sensibility, either sensuality or sensation, after reduction mammaplasty using a superior vertical dermal pedicle for the nippleareola complex. Sensuality was expressed by nipple erectility and sensation by areola contraction. Non parametric tests were used to analyze data concerning the return of sensibility for the nipple-areota complex. Return of sensibility for the nipple-areola complex, amount of the mammary tissue removed and elevation of the nipple-areola complex to its new position were compared.
Keywords: Nipple-areola complex; superior vertical dermal pedicle; sensuality; sensation.
RESUMO
Para avaliar a sensibilidade erógena e sensitiva do complexo aréolo-mamilar (CAM), após mamaplastia redutora empregando um retalho dérmico, vertical e de pedículo superior para suporte do CAM, foram realizados testes com agulha e toque suave com cotonete de algodão. A sensibilidade erógena foi expressada pela ereção do mamilo e a sensitiva pela contração da aréola e pela presença ou não de dor após a estimulação. Testes não paramétricos foram usados para analisar os dados referentes ao retorno da sensibilidade do CAM. O retorno da sensibilidade do CAM também foi avaliado em relação à quantidade de tecido mamário retirada e à elevação do CAM para a sua nova posição.
Palavras-chave: Complexo aréolo-mamilar; pedículo dérmico vertical superior; contração areolar; ereção do mamilo
Although many types of reduction mammaplasty have been described, few references concerning return of the sensation and sensuality of the nipple-areola complex after surgery have been reported(4). The nipple-areola complex receives its main nerve supply through intercostal
nerves. Sensation is supplied laterally by the lateral cutaneous branch of the III, IV, and V intercostal nerves and medially by the anterior cutaneous branch of the III, Iv, V, and VI intercostal nerves(9). The anterior and lateral branches of the cutaneous rami of the IV intercostal nerve pass through the subcutaneous tissue from the mammary circumference to the nipple areola complex, being specific to it(8). Sensation pro vided by supraclavicular branches of the cervical plexus has also been described for the nipple-areola complex(lO). Sensuality is supplied by the sympathetic nervous system(l2). It is realized through the fibers from the paravertebral ganglia to the second through the sixth intercostal nerves, to their final distribution to the smooth muscle present in the nipple(l2). Light pressure and crude touch were used for the qualitative measure of the nipple-areola complex sensibility(5). Needle test has also been employed to analyze the nipple-areola complex sensation(3). Another clinical evaluation concerning nipple-areola complex sensation has been performed comparing information related by the patients before and after the surgery(l). Schwarzmarm(ll) was the first to emphasize the importance of a dermal network for nipple-areola complex viability. Thereafter, many authors have developed dermal pedicles containing the nipple-areola complex as superior(2, 14), lateral(l3) or inferior(6) for reduction mammaplasty.
Evaluation of the return of the nipple-areola complex sensibility, either sensation or sensuality, after reduction.
mammaplasty using a dermal flap with superior vertical pedicle for the nipple-areola complex is described.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Reduction mammaplasty employing a pattern previously described(2) was used on thirty patients with ages ranging from 22 to 56 presenting asymmetrical hypertrophic breasts with a variable degree of ptosis. Table I sununarizes patient preoperative conditions and outcomes. The pattern creates a dermal flap with superior vertical pedicle for the nipple-areola complex (Fig. 1). It also defines the diameter and the new site of the nipple-areola complex, and the amount of mammary tissue to be removed. The superior pole of the breast was maintained intact. A test with fluorescein sodiwn 10% was used to determine vascular compromise of the nipple-areola complex. Light touch by cotton wool was applied to evaluate the nipple-areola complex sensibility, either to sensuality or to sensation (Fig. 2). Needle test was also applied to evaluate the nipple-areola complex sensibility, concerning areola sensation (Fig. 3).
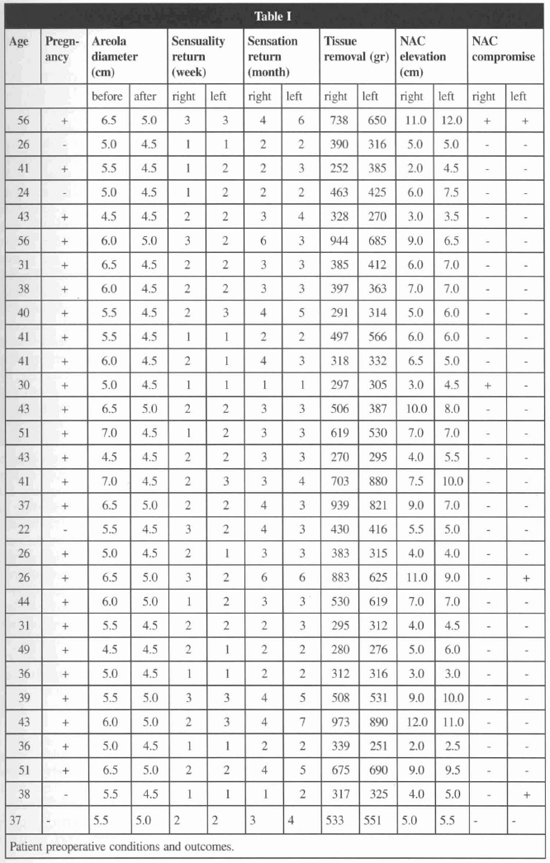
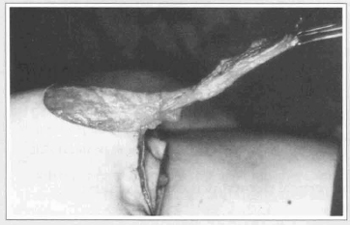
Fig. 1a - Dermal flap to the nipple-areola complex.
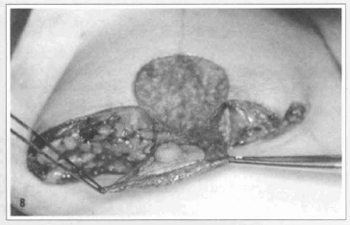
Fig. 1b - The pattern creates a superior vertical pedicle to the nipple-areola complex.
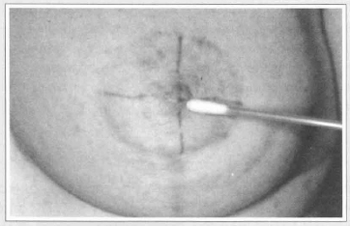
Fig. 2a - Light touch by cotton was used to evaluate either sensuality...
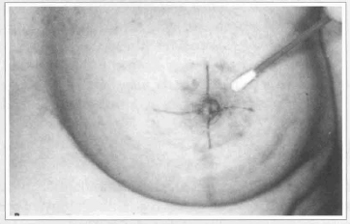
Fig. 2b - ... or sensation.
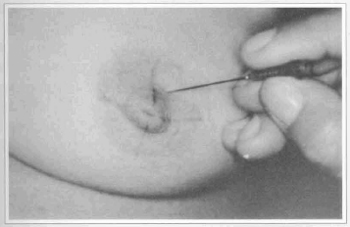
Fig. 3 -Needle test to evaluate areola sensation.
Sensuality was characterized by nipple erectility, and sensation by areola contraction and the degree of pain related by the patient (Fig. 4).
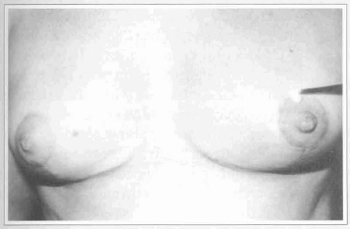
Fig. 4 - Light touch with cotton produces areola contraction on the left breast. No contraction is observed on the right breast.
To give a better evaluation for the areola sensation, the nipple-areola complex was divided into four quadrants: SLQ - superior lateral quadrant, SMQ - superior medial quadrant, ILQ - inferior lateral quadrant, IMQ -inferior medial quadrant (Fig. 5). Sensation was reported as absent or present through the contraction of the areola in each quadrant of the nipple-areola complex.
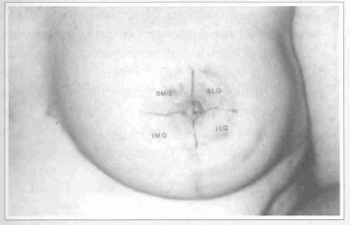
Fig. 5 - Nipple-areola complex divided into quadrants. SLQ - superior lateral quadrant. SMQ - superior medial quadrant. ILQ - inferior lateral quadrant. IMQ - inferior medial quadrant.
Sensation was also reported as present or absent in relation to the degree of pain reported by the patient in each quadrant of the nipple-areola complex. Data concerning areola sensation were provided through the areola contraction and the information mentioned by the patients every month after reduction mammaplasty, until sensibility was present in the four quadrants. Return of sensibility was analyzed and data compared with the amount of mammary tissue removed and nippleareola complex elevation. Non parametric tests were applied for analysis of the results and the respective level of significance was established for each test.
RESULTS
Sixty nipple-areola complex of thirty female patients had its diameters reduced with a variation from 4.5 to 5.0 cm and sustained by a dermal flap with superior vertical pedicle. Table I summarizes preoperative conditions and outcomes. Even though the test with fluorescein sodium does not reveal vascular compromise, five nipple-areola complex presented suffering, four in the inferior quadrants and one in the superior and inferior lateral quadrants. Reduction in the areola diameter did not affect the return of sensibility. Permanent loss of nipple erectility or areola contraction was not found in this group of patients. Decrease in the level of sensibility after reduction mammaplasty regarding the level of sensibility before the surgery was reported in five nipple-areola complex of four patients. Nipple erectility returned earlier than areola contraction and after 1 to 3 weeks from surgery (Fig. 6). Return of the nipple-areola complex sensation was more expressive (41/60) in the first 3 months after reduction mammaplasty (Fig. 7). Areola contraction and pain were recovered simultaneously on each quadrant of the nipple-areola complex, being present into the four quadrants until the sixth month after surgery. Only one nipple-areola complex recovered sensation seven months after reduction manunaplasty.
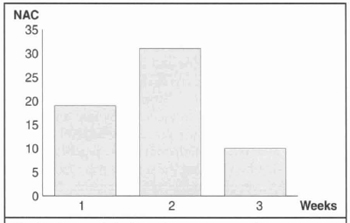
Fig. 6 - Return of nipple-areola complex sensuality.
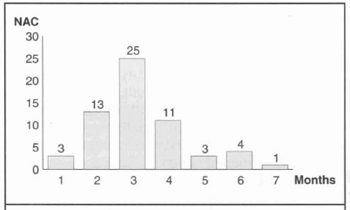
Fig. 7 - Return of nipple-areola complex sensation at monthly intervals.
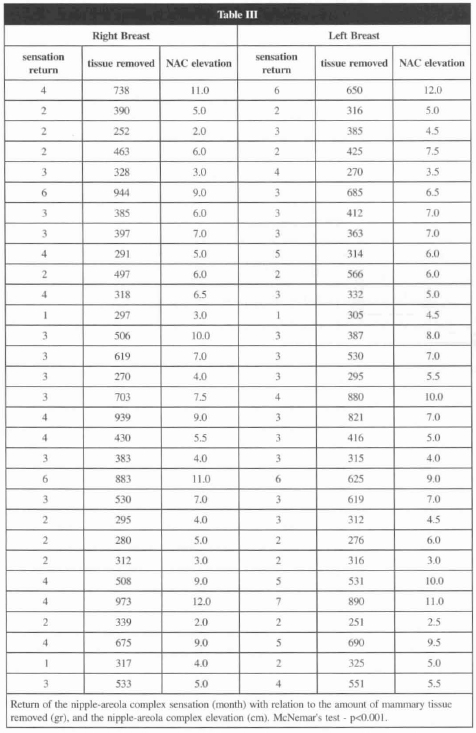
Cochran's test (p < 0.001) was employed to determine the level of significance of the return of sensation to each quadrant of the nipple-areola complex at monthly intervals. Table 2 shows monthly progressive increase in the return of sensation to each nipple-areola complex quadrant. McNemar's test (p < 0.001) was applied to compare return of sensation between the quadrants of the nipple-areola complex. Return of sensation on the superior quadrants was significantly higher than on the inferior quadrants (Fig. 8). Sensation in the superior medial quadrant returned first. McNemar's test (p < 0.001) was also applied to compare return of the nipple-areola complex sensation between both right and left breasts. No significant difference was observed. Spearm's coefficient (p < 0.003) was used to analyze return of nipple-areola complex sensation, measured in months, with regard to the amount of mammary tissue removed, quantitated in grams, and with regard to the nipple-areola complex elevation to its new position, measured in centimeters.
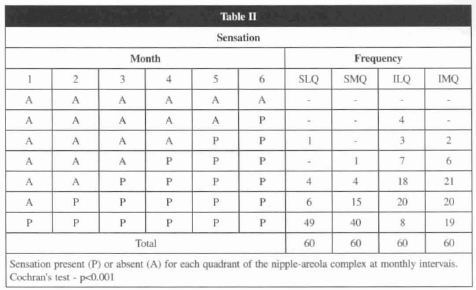
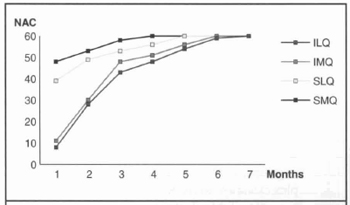
Fig. 8 - Return of sensation for each of the nipple-areola complex at monthly intervals.
Table 3 shows positive and significant correlation between return of sensation, amount of manunary tissue removed and elevation of the nipple-areola complex. Return of nipple-areola complex sensation was more delayed, the more elevated it was, and the more manunary tissue was removed.
A representative case is described in details.
A 41 year-old female, two pregnancies, presented asymmetrical large heavy and pendulous breasts(Fig. 9a). She was submitted to reduction mammaplasty with a superior vertical dermal pedicle for the nipple-areola complex with the diameter of the areola reduced from 7.0 to 4.5 cm. Sensation returned in the 3rd month on the right breast and in the 4th month on the left breast. The amount of mammary tissue removed was 703 g on the right breast and 880 g on the left one. Nipple-areola complex was elevated 7.5 cm on the right breast and 10.0 cm on the left breast. At the end of the first postoperative year the nipple-areola complex remains in its position (Fig. 9b).
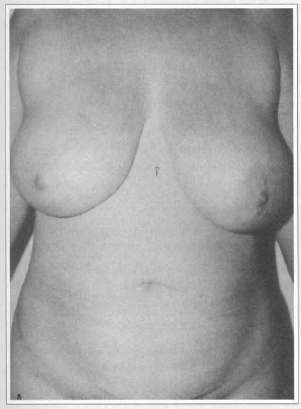
Fig. 9a - Preoperative frontal view of asymmetrical large heavy pendulous breasts.
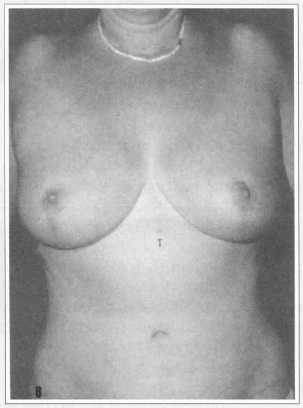
Fig. 9b - I year postoperative frontal view. Nippleareola complex elevation can be evaluated comparing its location before and after surgery in relation to the natural sign pointed by the arrow.
DISCUSSION
The breast, operated or not, has an irregular pattern of sensation and is not completely understood(7). Despite an anatomical correlation between both sensibility parameters, sensuality returned before sensation. Mechanical stimulation of the nipple initiates a neural transmission, which by a reflex arch through the intercostal nerve, induces smooth muscle contraction with earlier nipple erectility.
Mechanical stimulation of the areola starts the same neural transmission; however, delay in the return of the areola contraction in relation to the nipple erectility probably occurs by the absence of a reflex arch in this neural transmission. Maintenance of the whole superior pole of the breast attached to the pectoral muscle preserves the cutaneous branches of the III and IV intercostal nerves. This assures nipple-areola complex sensibility through the dermal flap with superior vertical pedicle. Since the pedicle had a superior position, nipple-areola complex sensation returned earlier for the superior quadrants. Decrease in the level of sensibility after the surgery reported in 5 nipple-areola complex occurs in the nipple-areola complex that presented vascular compromise. Delay in the recovery of nipple-areola complex sensibility was associated with the amount of mammary tissue removed, and the elevation of the nipple-areola complex to its new position.
REFERENCES
1. Abramo AC. Mamaplastia redutora corn pediculo dérmico vertical superior. Tese para obtenção do Titulo de Mestrado pela Escola Paulista de Medicina. 1988; 1-108.
2. __. Pattern for Reduction Mammaplasty that Uses a Superior Vertical Dermal Pedicle. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 1991; 15:265-70.
3. Abramo AC, Viola JC. Avaliação da Sensibilidade do Complexo Areolo-mamilar após Mamaplastia Redutora. An. Paul. Med. Cir. 1993; 120:9-13.
4. Castro CC, Araujo MR. Avaliação dos Resultados Tardios em Mamoplastia. Rev. Bras. Cir. 1983; 73:21-5.
5. Courtiss EH, Goldwyn RM. Breast Sensation Before and After Plastic Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1976; 58:1-13.
6. __. Reduction mammaplasty by the inferior technique. An alternative to free nipple and areola grafting for severe macromastia or extreme ptosis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1977; 59:501-7.
7. Giebel GD, Jaeger K. Sensibilitatsmessungen vor und nach Mammareduktions-plastic zweier Konkurriezender Operationverfahren. Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1986; 359:299-301.
8. Hagerty RC, Hagerty RF. Reduction Mammoplasty: Central Cone Technique for Maximal Preservation of Vascular and Nerve Supply. South Med. J. 1989; 82: 183-6.
9. Lockhart RD, Hamilton GF, Fyfe FW. Anatomy of the Human Body. 1959; 2 ed, London, Faber and Faber. 274-81.
10. Rees TD. Plastic Surgery of the Breast. IN: Converse JM. Reconstructive Plastic Surgery. 1966; Philadelphia and London, WB Saunders Company. 1903-38.
11. Schwarzmann E. Die Technic der Mamoplastic. Chirurgentagung. 1930; 2:932-6.
12. Serafin D. Surgical Anatomy of the Breast. IN: Gerogiade NG. Breast Reconstruction Following Mastectomy. 1979; St. Louis, Toronto, London, The C.V. Mosby Company. 35-53.
13. Skoog T. A Technique of the Breast Reduction. Acta Chir. Scand. 1963; 126:453-7.
14. Weiner DL, Aiache AE, Silver L, Tittiranonda T. A Single Dermal Pedicle for Nipple Transposition in Subcutaneous Mastectomy or Mastopexia. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1973; 51: 115-20.
I - Doctor in Plastic Surgery by Escola Paulista de Medicina, UNIFESP Head Professor of ACA - Grupo Integrado de Assistencia em Cirurgia Plastica at Beneficencia Portuguesa.
II - Resident doctors of ACA - Grupo Integrado de Assistencia em Cirurgia Plastica.
Address for correspondence:
Antonio Carlos Abramo, MD
R. Afonso de Freitas, 641
04006-052 - São Paulo - SP Brazil


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter